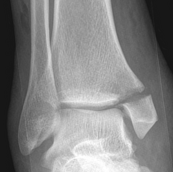
Fracture patterns
| Lateral malleolar fractures | Medial malleolar fractures | Bimalleolar fractures | Trimalleolar fractures |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Weber A - below syndesmosis Weber B - at syndesmosis Weber C - above syndesmosis |
Uncommon |
Fibular + medial malleolus Bimalleolar equivalent - fibular + deltoid ligament Fibular + posterior malleolus |
Fibular fracture + Medial malleolus fracture + Posterior malleolus fracture |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Anatomy
Ligaments
| Lateral Ligament Complex | Deltoid ligament | Sydesmosis |
|---|---|---|
|
ATFL CFL PTFL |
Superficial deltoid Deep deltoid |
AITFL PITFL Interosseous ligament Transverse tibiofibular ligament
|
Biomechanics
| Load | ROM | Dorsiflexion | Plantarflexion |
|---|---|---|---|
|
90% load through plafond to talus 10% load through lateral talofibular articulation |
Dorsiflexion 30° Plantarflexion 45° |
Talus wider anteriorly 2.5 mm Fibula moves laterally & ER to accommodate
|
Deltoid ligament prevents ER of talus 5° internal rotation talus |
- 1mm lateral talus shift
- ankle contact area decreased by 40%
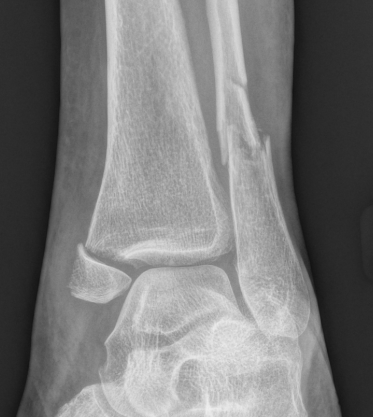
Ankle Fracture Classification
Weber Classification of fibular fractures
| Weber A | Weber B | Weber C |
|---|---|---|
| Fracture distal to syndesmosis | Fracture at level of syndesmosis | Fracture above level syndesmosis |
|
Stable - avulsion fracture |
Stability depends on deltoid ligament
Stable - no increased medial clear space / deltoid ligament intact Unstable - Increased medial clear space / deltoid ligament rupture |
Unstable
Syndesmosis disrupted |
 |
  |
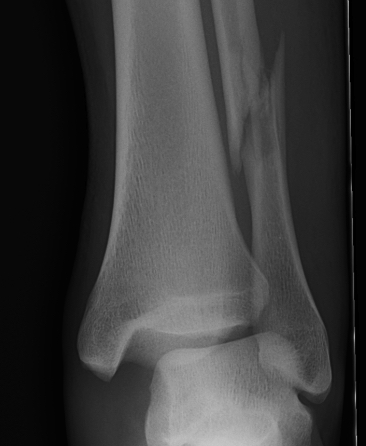 |
Lauge-Hansen Classfication
Two part
1. Position of talus - pronation / supination
2. Direction of force - external rotation or translational (adduction / abduction)
| Supination-Adduction | Supination-External Rotation | Pronation-Abduction | Pronation-External Rotation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Stage 1: Weber B fibula |
Stage 1: Rupture of AITFL
|
Stage 1: Deltoid ligament rupture / transverse fracture of the medial malleolus |
Stage 1: Deltoid ligament rupture / transverse fracture of the medial malleolus
|
| Stage 2: Vertical medial malleolus | Stage 2: Weber B fibular | Stage 2: Rupture of the AITLF / PITFL or bony avulsion | Stage 2: Rupture of the AITFL or bony avulsion |
| Stage 3: Rupture of PITFL / fracture of posterior malleolus | Stage 3: Weber C fibula (often butterfly) | Stage 3: Spiral/Oblique fracture Weber C | |
| Stage 4: Transverse fracture of medial malleolus | Stage 4: Rupture of the PITFL or fracture of the posterior malleolus | ||
| Most common - up to 85% all injuries | Less than 5% of ankle fractures | ||
 |
 |
 |
 |
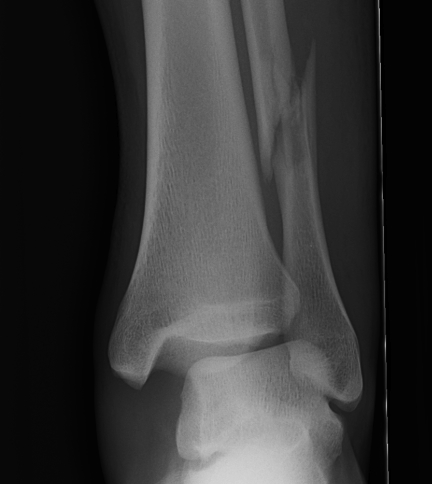
X-ray assessment
3 standard views
AP / Lateral / Mortise
Mortise
- AP with foot internally rotated
- should be symmetrical space around talus
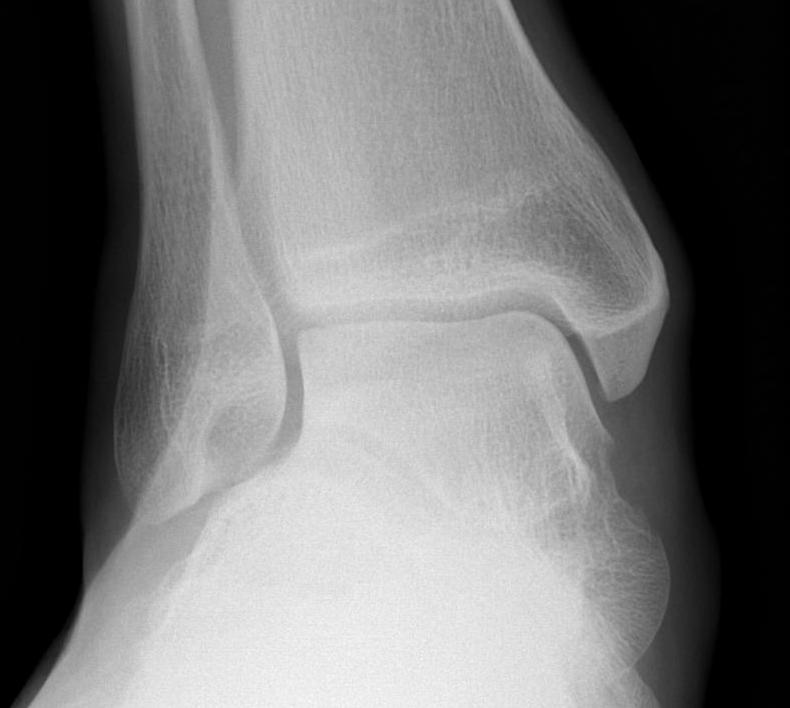
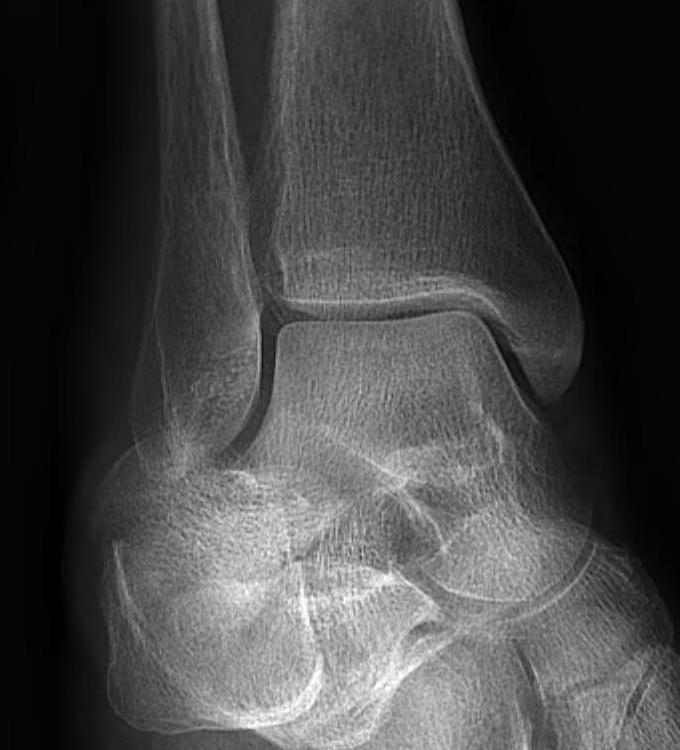
| Increased tibio-fibular clear space | Overlap | Increased medial clear space |
|---|---|---|
|
Medial border of the fibula Lateral border of the posterior tibia (incisura fibularis) Measured 1 cm above the plafond |
Overlap of the fibula and the anterior tibial tubercle
|
Medial talus to lateral medial malleolus |
| <5mm AP and mortise |
> 6 mm AP view > 1 mm mortise view |
< 4mm Equal to superior clear space |
| Syndesmotic injury | Syndesmotic injury |
Deltoid ligament injury Lateral talar shift |
 |
 |
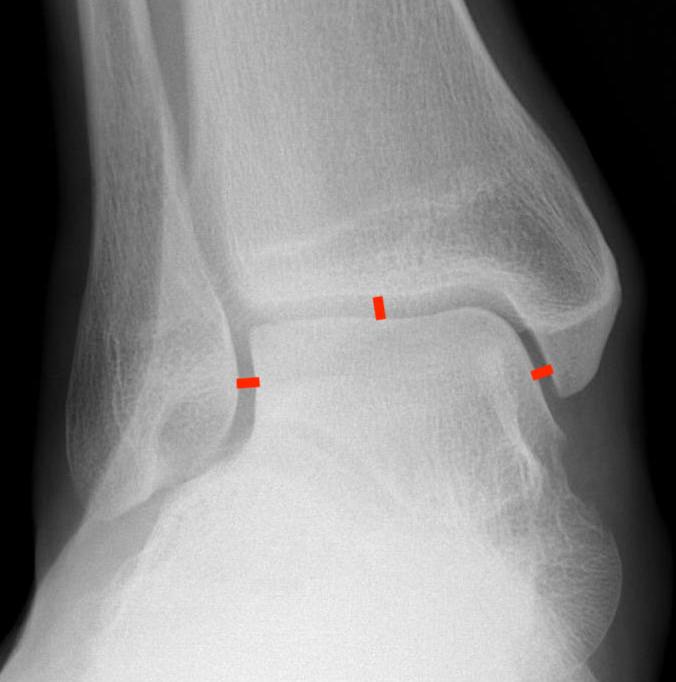 |
Lateral talar shift / increased medial clear space / deltoid ligament injury
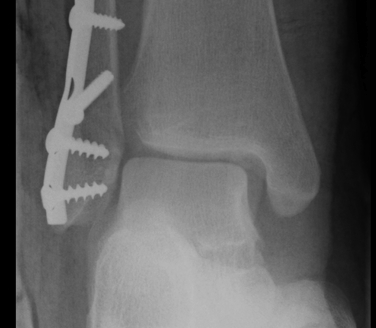


Tibia / fibular overlap < 1mm / syndesmotic injury


Management
Ankle dislocation
Reduction under conscious sedation
- protects skin medially
- conscious sedation in emergency department
- well moulded cast
- unstable ankles need monitoring for loss of reduction
- can need external fixation to maintain position



External fixation
Unstable reduction / swelling / poor skin / blisters
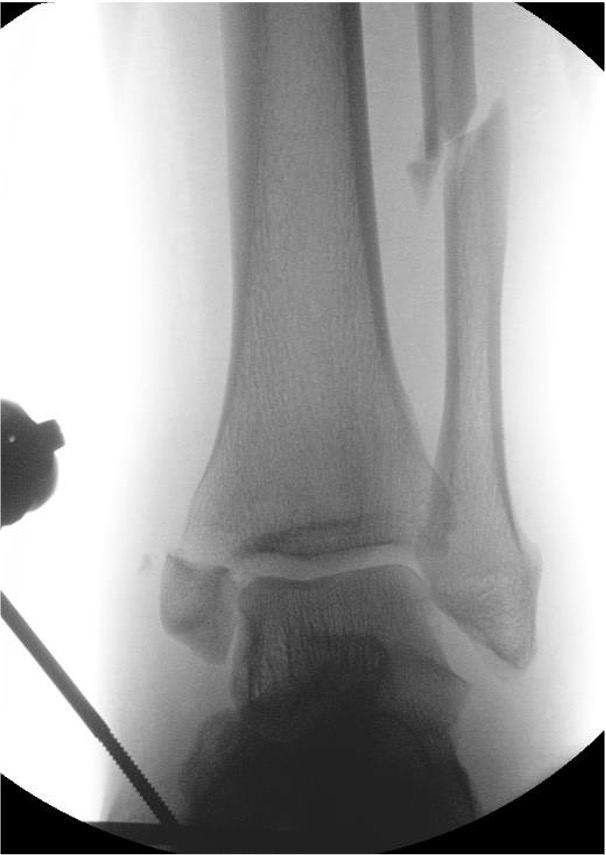
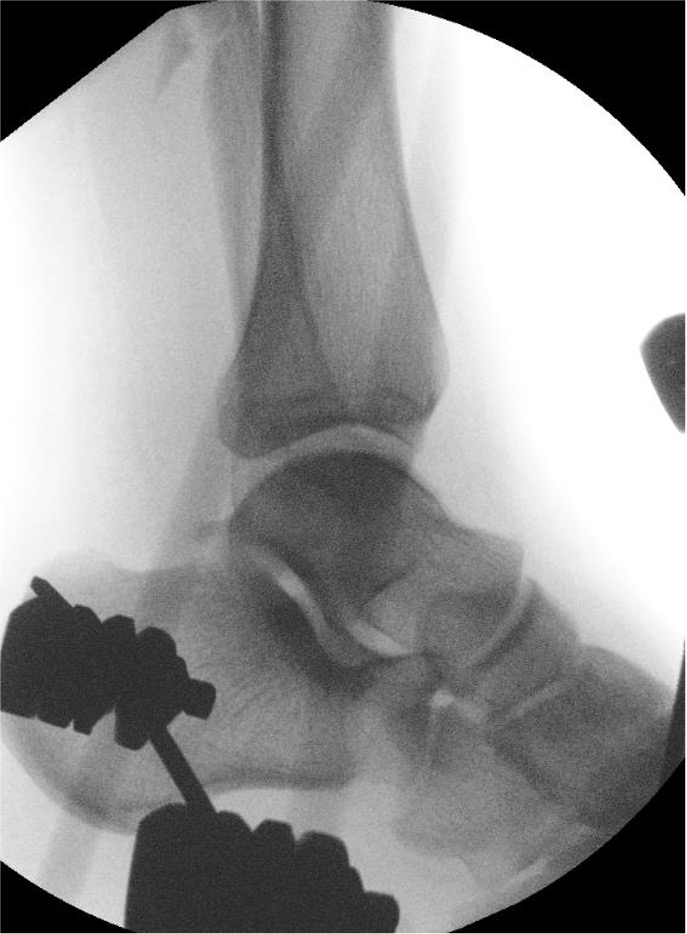





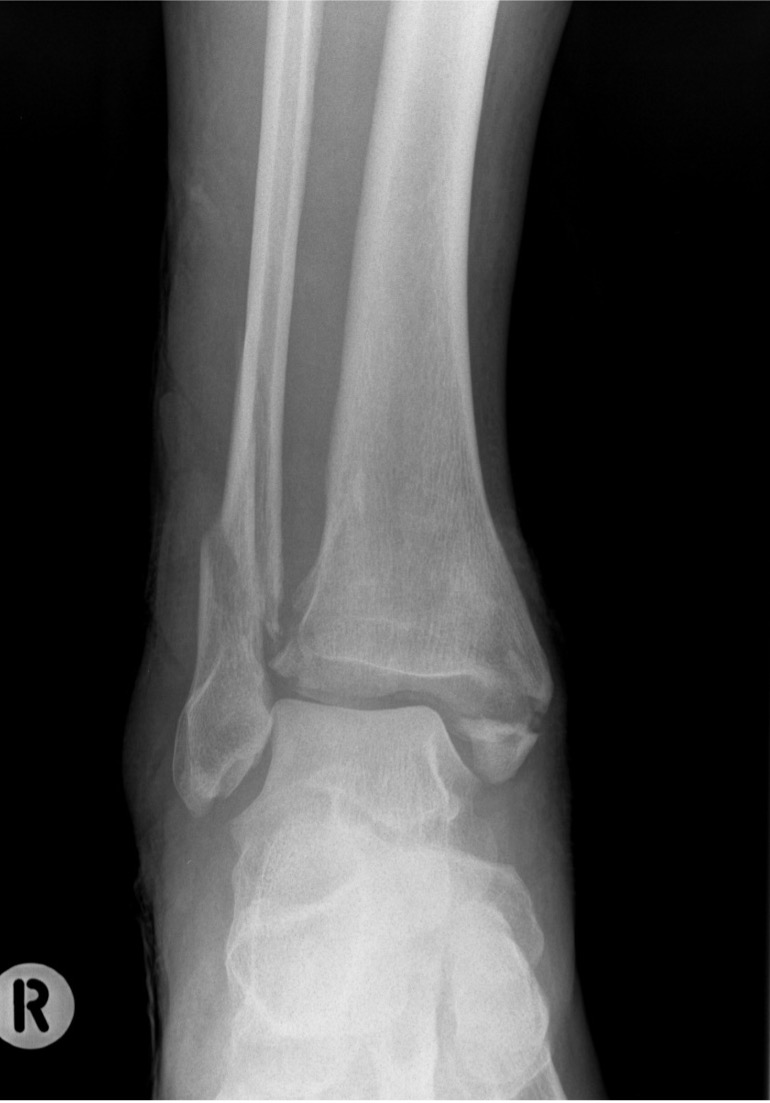
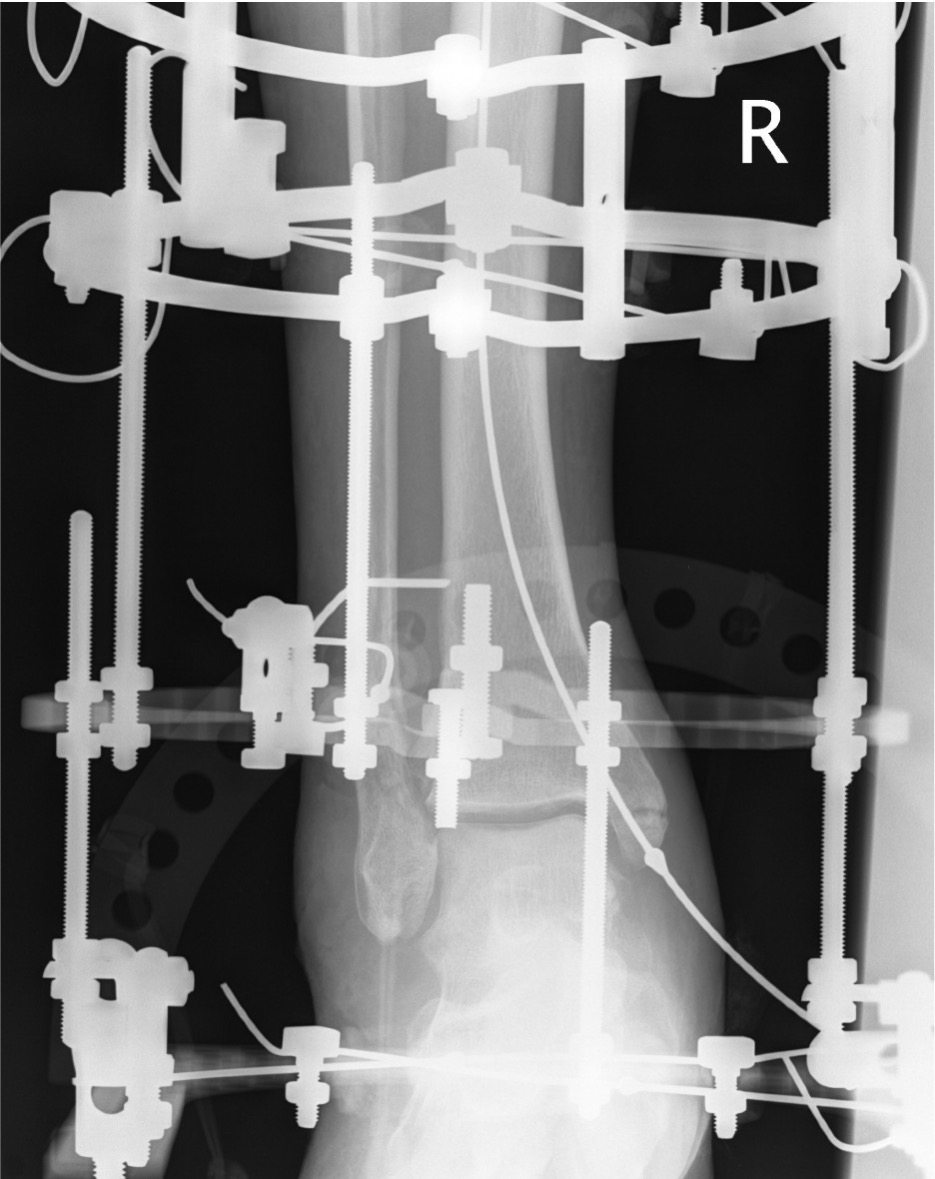

Compound fractures

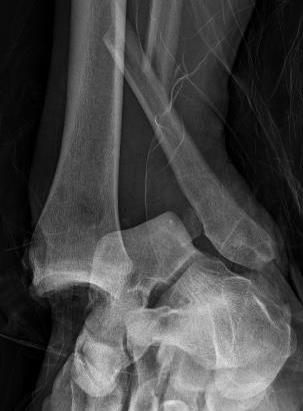

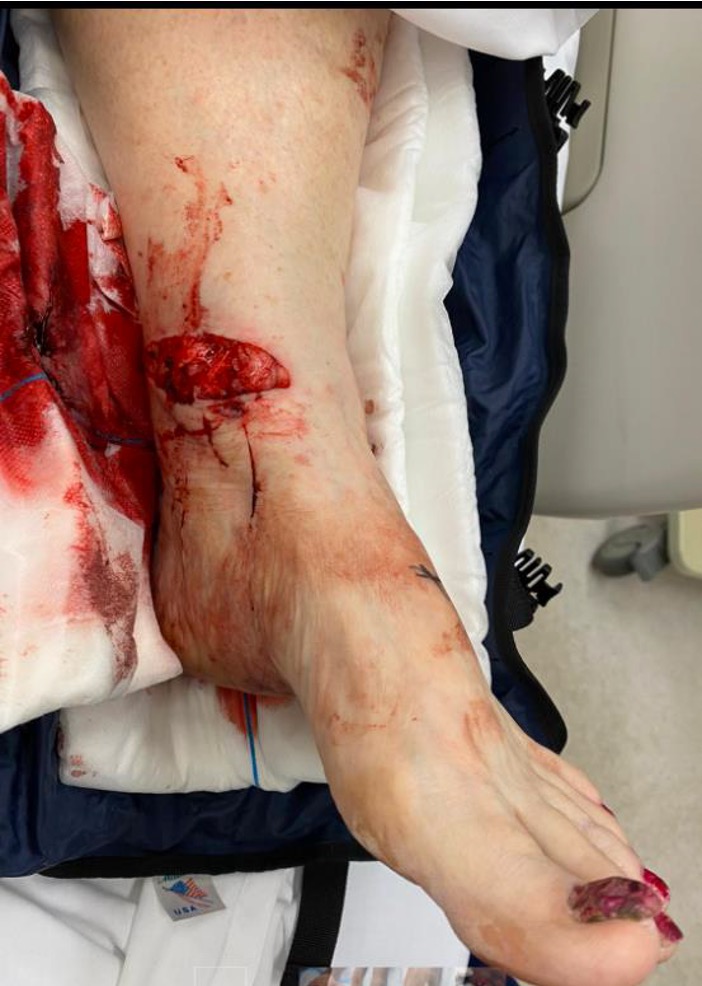
Results
Martin et al J Orthop Trauma 2021
- 41 open ankle dislocations with medial wound
- pronation-abduction
- 10% deep infection, one amputation
- 22 open pronation-abduction injuries compared with 35 other open ankle fractures
- pronation abduction group associated with obesity, reoperations, arthrodesis and ampution
Operative Management
Diabetes / elderly / fragility fractures
Issues
High risk infection / wound complications / loss of fixation
See boneschool page - Fragility Fractures
Timing of surgery
Operate when swelling reduced / wrinkling / resolution of blisters
- risk not being able to close wounds / infection
- higher risk with bimalleolar / 2 incision operations
Schepers et al Int Orthop 2013
- prospective study of ankle fracture surgery
- infection rate surgery < 1 day: 0/60
- infection rate delayed surgery: 16/145 (11%)
- infection rate surgery < 1 week: 2%
- infection rate surgery > 1 week: 13%
Skin preparation
- RCT of iodine v chorhexidine prep
- 6700 patients undergoing lower limb fracture surgery (~8% ankles)
- closed fracture infections: iodine 2.4%, chlorhexidine 3.3%
- open fracture infections: iodine 6.5%, chorhexidine 7.3%
Early Weight bearing
Sharma et al Foot Ankle Surg 2022
- early versus delayed weight bearing
- meta-analysis of 14 RCTs
- early weight bearing had better short term outcomes at 6 - 9 weeks
- no difference at 6 months
- early return to work with early weight bearing
Baumbach et al Foot Ankle Surg 2023
- early versus delayed weight bearing
- meta-analysis of 13 studies
- early weight bearing did not increase complication rate
Early ROM
Keene et al J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2014
- meta-analysis of immobilization versus early ROM
- 11 studies
- no difference in functional outcomes at 6 weeks, 3 months or 1 year
- reduced DVT with early ROM
- increased infection / fixation failure / removal of metalwork with early ROM
Complications
Infection


- systematic review of 10 studies and 8000 operative fixation ankle fractures
- incidence infection 7%
- increased with: open fractures / fracture dislocations / high energy injuries
- increased with: increased BMI, ASA 3, diabetes, smoking
DVT / PE
Blanco et al J Foot Ankle Surg 2018
- prospective cohort and 90 incidence of DVT / PE
- achilles tendon in cast: 5%
- ankle fracture cast / no surgery:2%
- ankle fracture surgery: 3%
Elliott et al Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2023
- 483 patients with surgically treated ankle fractures
- DVT / PE no prophylaxis: 3.5%
- DVT / PE with prophylaxis: 4%
- no difference in complications
Osteoarthritis
Swierstra et al EFORT Open Rev 2022
- systematic review
- overall incidence of post-traumatic OA 25%
Beak et al Foot Ankle Int 2022
- risk factors for OA in 330 patients
- increased risk with fracture dislocations / posterior malleolar fractures / malreduction

